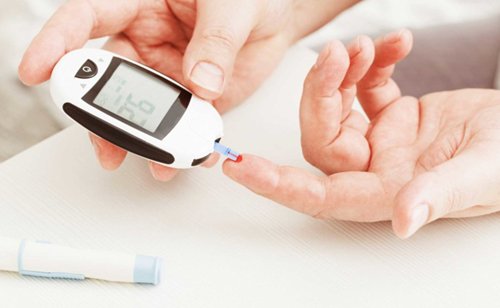
Diabetes mellitus (DM), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period.Symptoms of high blood sugar include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased hunger.If left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications.Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death.Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, and damage to the eyes.
Signs and symptoms
The classic symptoms of untreated diabetes are unintended weight loss, polyuria (increased urination), polydipsia (increased thirst), and polyphagia (increased hunger).Symptoms may develop rapidly (weeks or months) in type 1 diabetes, while they usually develop much more slowly and may be subtle or absent in type 2 diabetes. Other symptoms of diabetes mellitus include weight loss and tiredness
Prevention
There is no known preventive measure for type 1 diabetes.Type 2 diabetes—which accounts for 85–90% of all cases worldwide—can often be prevented or delayed by maintaining a normal body weight, engaging in physical activity, and eating a healthy diet.Higher levels of physical activity (more than 90 minutes per day) reduce the risk of diabetes by 28%.Dietary changes known to be effective in helping to prevent diabetes include maintaining a diet rich in whole grains and fiber, and choosing good fats, such as the polyunsaturated fats found in nuts, vegetable oils, and fish.Limiting sugary beverages and eating less red meat and other sources of saturated fat can also help prevent diabetes.Tobacco smoking is also associated with an increased risk of diabetes and its complications, so smoking cessation can be an important preventive measure as well.

